My thanks to Paul for this article, I hope you all enjoy reading it and learn something about the black stuff that helps power our steam locomotives.
By Paul Roe Locomotive Department Manager
Coal is very much in the news at the moment as the UK ceases to mine its own coal, some say we are facing a coal crisis and soon we won’t have any coal left and Heritage railways will soon struggle to operate. This is far from correct and coal is and will still be imported from other parts of the world, the ironic issue being the carbon footprint is much larger importing coal then actually mining it in the UK. Many years ago in the heyday of coal mining, people were scared that if mining continued the UK would float and float away
Coal is classified into four main types, or ranks: anthracite, bituminous, subbituminous, and lignite. The ranking depends on the types and amounts of carbon the coal contains and on the amount of heat energy the coal can produce. The United States holds the world’s biggest coal reserves. The nation’s proved coal reserves as of December 2018 stood at 250.2 billion tonnes (Bt) accounting for approximately 24% of the worlds proven coal reserves. Anthracite is found on the east coast in the US, South Africa, Australia, Western Canada, China and Russia. Two-thirds of Russia’s coal reserves are anthracite. Because of its efficiency and thus less carbon and sulphur usage per watt of power, anthracite is also the ‘cleanest’ coal in the world.
The NVR over the years have used coal from across the Globe, we have used Scottish, Welsh, Cumbrian, Russian, Polish, Bosnian. By far the cleanest is Welsh Steam coal, this coal provides high heat and less smoke, but is more expensive and takes a longer time to combust, so as a fireman you have to think about boiler management earlier than using a non-steam coal. At present a tonne of coal is averaging at £175 a tonne plus vat, coal consumption is different on each locomotive and several factors come in to play, size of boiler and firebox, how the driver operates the locomotive, the load that is being hauled, steam heat, is the coal of good source? So coal steams are terrible and the coal will just not burn hot. A locomotive the size of 92 Squadron would use up to about 1 tonne of coal per trip on the NVR, if the locomotive is running not stop less coal would be used and the locomotive would be working more efficiently. Currently the NVR is running on Scottish coal, this is a good coal but can be smoky coal, this can be controlled by the fireman, if you see dark thick black smoke, this would indicate that the fireman has over fired and not enough air is entering the firebox to burn the gasses away.
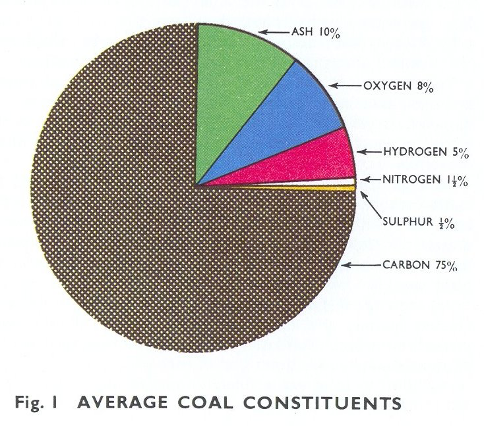
Composition of Air and Coal
Combustion takes place when coal burns in air, and correct combustion can only be obtained by bringing together the right amounts of coal and air at the same time. To examine this statement more fully it is necessary that we should know something of the chemical constituents of coal and air.
Coal varies in quality and composition, but the greater part of it consists of carbon, the remainder being composed of gases and ash (see Fig. 1).
Air consists of a mixture by weight of approximately 23% oxygen and 77% nitrogen, or when measured by volume, 21% oxygen and 79% nitrogen.
Coal comes in all different sizes and the ideal size of coal for burning on a steam locomotive is “The size of a man’s fist”, anything any bigger will take longer to burn and can make cold spots in the fire bed, we are currently in stock with coal on the NVR we about 35 tonnes of Scottish coal on site, this will soon be added to with about 28 tonnes of Northumberland coal which is being provided by West Coast Rail and a very good price. The Miniature Railway at Wansford operates on anthracite coal and these are the size of beans, anthracite is used on all steam models and it is smokeless so this stops the smaller boiler tubes furring up and creates a high temperature for the smaller fireboxes
